kwimage.im_stack module¶
Functions for stacking images (of potentially different sizes) together in a single image.
Notes
We may change the “bg_value” argument to “bg_color” in the future.
- kwimage.im_stack.stack_images(images, axis=0, resize=None, interpolation=None, overlap=0, return_info=False, bg_value=None, pad=None, allow_casting=True)[source]¶
Make a new image with the input images side-by-side
- Parameters:
images (Iterable[ndarray]) – image data
axis (int) – axis to stack on (either 0 or 1)
resize (int | str | None) – if None image sizes are not modified, otherwise resize resize can be either 0 or 1. We resize the resize-th image to match the 1 - resize-th image. In other words, resize=0 means the current image is resized to match the next image, and resize=1 means the next image is resized to match the current image. Can also be strings “larger” or “smaller”. If resize=”larger”, the current image is only resized if the next image is larger. If resize=’smaller’ the current image is resized only if the next image is smaller. TODO: this needs to be reworked to be more intuitive.
interpolation (int | str) – string or cv2-style interpolation type. only used if resize or overlap > 0
overlap (int) – number of pixels to overlap. Using a negative number results in a border.
pad (int) – if specified overrides overlap as a the number of pixels to pad between images.
return_info (bool) – if True, returns transforms (scales and translations) to map from original image to its new location.
bg_value (Number | ndarray | str) – background value or color, if specified, uses this as a fill value.
allow_casting (bool) – if True, then if “uint255” and “float01” format images are given they are converted to “float01”. Defaults to True.
- Returns:
an image of stacked images side by side
- Tuple[ndarray, List]: where the first item is the aformentioned stacked
image and the second item is a list of transformations for each input image mapping it to its location in the returned image.
- Return type:
ndarray
Todo
- [ ] This is currently implemented by calling the “stack_two_images”
function multiple times. This should be optimized by allocating the entire canvas first.
Example
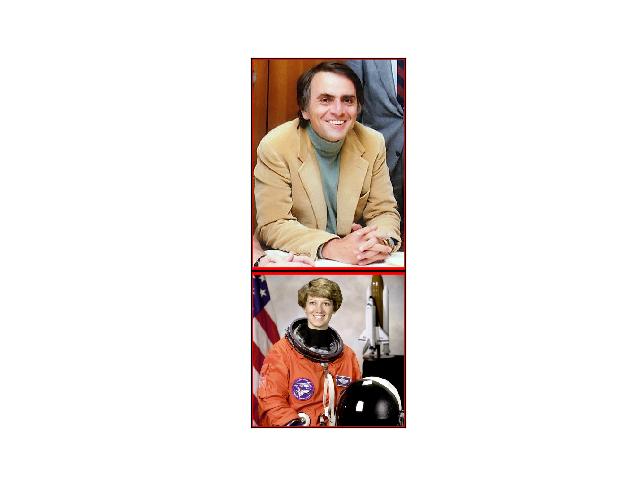
>>> import kwimage >>> img1 = kwimage.grab_test_image('carl', space='rgb') >>> img2 = kwimage.grab_test_image('astro', space='rgb') >>> images = [img1, img2] >>> imgB, transforms = kwimage.stack_images( >>> images, axis=0, resize='larger', pad=10, return_info=True) >>> print('imgB.shape = {}'.format(imgB.shape)) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:kwplot) >>> import kwplot >>> import kwimage >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> kwplot.imshow(imgB, colorspace='rgb') >>> wh1 = np.multiply(img1.shape[0:2][::-1], transforms[0].scale) >>> wh2 = np.multiply(img2.shape[0:2][::-1], transforms[1].scale) >>> xoff1, yoff1 = transforms[0].translation >>> xoff2, yoff2 = transforms[1].translation >>> xywh1 = (xoff1, yoff1, wh1[0], wh1[1]) >>> xywh2 = (xoff2, yoff2, wh2[0], wh2[1]) >>> kwplot.draw_boxes(kwimage.Boxes([xywh1], 'xywh'), color=(1.0, 0, 0)) >>> kwplot.draw_boxes(kwimage.Boxes([xywh2], 'xywh'), color=(1.0, 0, 0)) >>> kwplot.show_if_requested()

- kwimage.im_stack.stack_images_grid(images, chunksize=None, axis=0, overlap=0, pad=None, return_info=False, bg_value=None, resize=None, allow_casting=True)[source]¶
Stacks images in a grid. Optionally return transforms of original image positions in the output image.
- Parameters:
images (Iterable[ndarray]) – image data
chunksize (int) – number of rows per column or columns per row depending on the value of axis. If unspecified, computes this as int(sqrt(len(images))).
axis (int) – If 0, chunksize is columns per row. If 1, chunksize is rows per column. Defaults to 0.
overlap (int) – number of pixels to overlap. Using a negative number results in a border.
pad (int) – if specified overrides overlap as a the number of pixels to pad between images.
return_info (bool) – if True, returns transforms (scales and translations) to map from original image to its new location.
resize (int | str | None) – if None image sizes are not modified, otherwise can be set to “larger” or “smaller” to resize the images in each stack direction.
bg_value (Number | ndarray | str) – background value or color, if specified, uses this as a fill value.
allow_casting (bool) – if True, then if “uint255” and “float01” format images are given they are converted to “float01”. Defaults to True.
- Returns:
an image of stacked images in a grid pattern
- Tuple[ndarray, List]: where the first item is the aformentioned stacked
image and the second item is a list of transformations for each input image mapping it to its location in the returned image.
- Return type:
ndarray
- SeeAlso:
Example
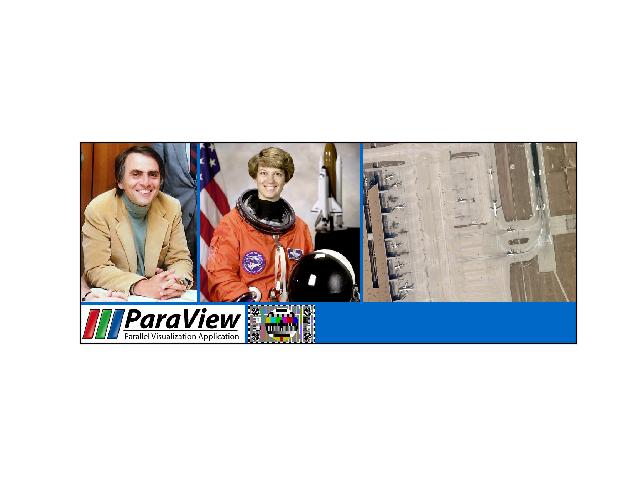
>>> import kwimage >>> img1 = kwimage.grab_test_image('carl') >>> img2 = kwimage.grab_test_image('astro') >>> img3 = kwimage.grab_test_image('airport') >>> img4 = kwimage.grab_test_image('paraview')[..., 0:3] >>> img5 = kwimage.grab_test_image('pm5644') >>> images = [img1, img2, img3, img4, img5] >>> canvas, transforms = kwimage.stack_images_grid( ... images, chunksize=3, axis=0, pad=10, bg_value='kitware_blue', ... return_info=True, resize='larger') >>> print('canvas.shape = {}'.format(canvas.shape)) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> import kwimage >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas) >>> kwplot.show_if_requested()
- kwimage.im_stack._stack_two_images(img1, img2, axis=0, resize=None, interpolation=None, overlap=0, bg_value=None, allow_casting=True)[source]¶
- Returns:
imgB, offset_tup, sf_tup
- Return type:
Tuple[ndarray, Tuple, Tuple]
- kwimage.im_stack._efficient_rectangle_packing()[source]¶
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Packing_problems https://github.com/Penlect/rectangle-packer https://github.com/secnot/rectpack https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1213394/what-algorithm-can-be-used-for-packing-rectangles-of-different-sizes-into-the-sm https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/210979/Fast-optimizing-rectangle-packing-algorithm-for-bu
- Requires:
pip install rectangle-packer